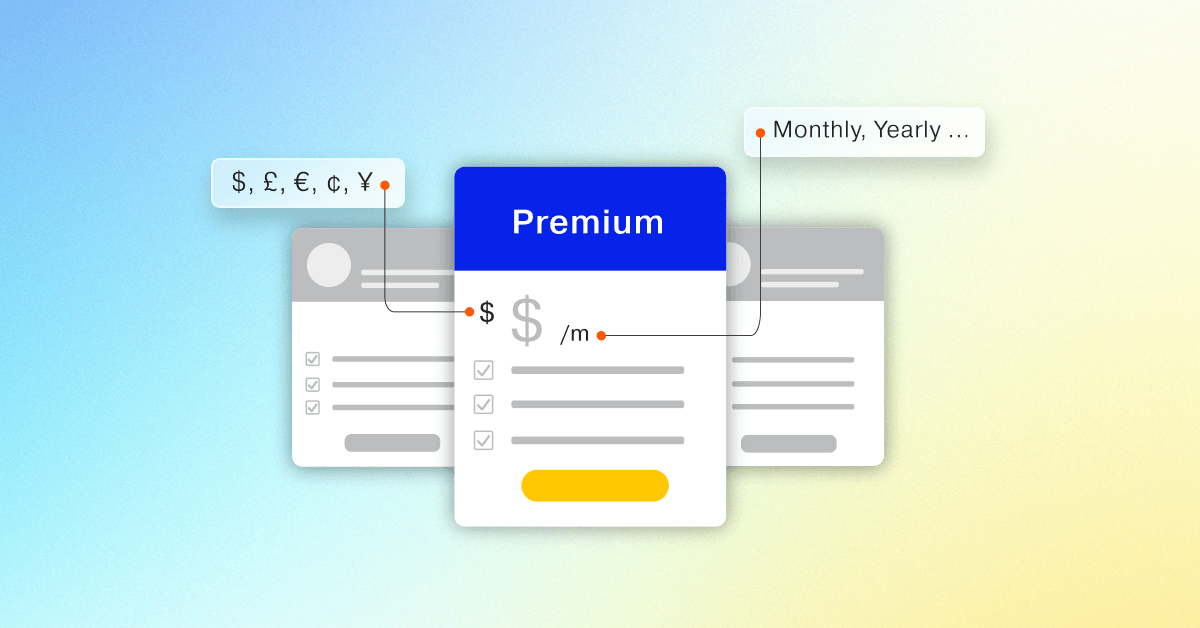
Define subscription and billing management
Subscription and billing management is the method of handling of a subscription’s entire lifecycle for a customer and charging them throughout the agreement. In other words, subscription management is the art of managing your customer’s lifecycle with your company. It begins when a customer signs up for or purchases your product or service and ends at the point where they cancel or leave the subscription.
During the subscription period, subscriptions can be upgraded, downgraded, amended, paused, and undergo many other types of modifications. Billing management is the process of a business tracking and managing invoices and accounts across any number of customers and can involve multiple billing management solutions.
What is a subscription?
A subscription is a service contract or agreement between a vendor (seller) and a customer (buyer) for the rights to use a product or service or combination of both (known as a bundle) for a specific timeframe. The subscription starts when the customer signs up to the vendors product, service, or bundle, and ends when the customer cancels the service, depending on the specific terms of the agreement.
Subscriptions are either manually managed or by a subscription management software or platform.
What is not subscription management?
Subscription management is not simply taking care of recurring billing and payments for products or solutions bought by a customer on more than one occasion. In fact, subscription management covers all the changes, processes, and complexities that arise with a subscription as it moves through its lifecycle from beginning to end, including changes and updates to its terms, pricing, duration and more.
Why is subscription management important?
While there are several reasons subscription management is important, including creating efficient processes, accurate accounting, timely delivery and an improved customer experience.
Subscription management as a business model is important to key channel players, including telcos, MSPs and IT distributors, today from a business strategy perspective for three main reasons:
- The IT market has shifted from products to subscriptions, and as of 2022, the XaaS subscription model is generating 77% of gains from customers
- Self service capabilities for SMBs can help make their IT spend go further
- As a key channel offering, subscriptions align with the shared and circular economy
What is a subscription model?
A subscription model is a strategic business approach that involves selling the rights to use a product or solution for a period of time in order to generate recurring revenue on a period basic, whether per month or year.
What is PIM?
PIM stands for product information management. It’s an important concept in relation to subscriptions because PIM is the process of maintaining and distributing critical information about a product or solution as changes arise.
As the process flow can become quite complicated, a PIM platform can be used to create efficiencies through automation. Learn more about PIM how to reduce product information management (PIM) complexity.
What are some other important concepts and terms to know for subscription management?
The pricing and billing model for subscriptions is typically structured with a tier based on features or numbers of users. Often, companies choose to bill with two models: either usage-based or freemium. Incremental revenue can be made from potential add-ons—one way is to create XaaS bundles, though creating these bundles can cause some complexity without the use of a subscription platform.
Some typical processes during an active subscription include:
- Proration: Charging your customers only for the period they have used your product or service
- Communication: Making effective and ongoing communication with your customer one of your top priorities
- Engagement: Reaching out to your customer to make periodic contact, whether by phone, email or automated notifications
- Payment: Staying on top of revenue collection either manually or using automation
- Grace periods: Handling the extension of time to make payments, either by personal contact or through automation
Some of the typical processes following a subscription period include:
- Feedback: Collecting insights on your customer’s experience
- Renewal: Moving the subscription through its renewal phase either manually or with your subscription platform
How can subscription management help you?
Telcos, MSPs and IT distributors are faced with their own set of challenges and opportunities. Deciding to create or grow an XaaS marketplace can help you capture more ARPU as margins tighten due to a saturated market.
The path of offering and managing XaaS subscriptions opens up new revenue opportunities from sales of cloud solutions, delighting customers with the solutions they need and establishing yourself as the one partner they need to source all of their technology. As a result, you can better overcome the issue of customer churn by increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Traditional Offerings
What are the market challenges for channel players
TELCOS
- Saturated market with lack of customers and low margins
- Lack of opportunity for growth and scalability
- Striving to become the one solution provider of choice
MSPs
- Low margins
- Making the transition from product selling to solution selling
- Difficulty in competing for new customers against competitors
IT DISTRIBUTORS
- Low margins (2-5% on average)
- Decreased growth and low scalability
- Reduced efficiency and higher operational costs
ISVs
- Standing out among competitors
- Generating capital to support growth
- Reaching new partners to scale the business
TECH VENDORS
- Increase margins and recurring revenue
- Provide more value beyond hardware and standard solutions
- Find ways to reach new customers and markets
XaaS Subscription Offerings
What are the market opportunities for channel players
TELCOS
- Entering three markets with stellar growth opportunities, cybersecurity ($139B), cloud ($445B) and IoT ($384B)
- Make scalability possible with end-to-end automation of subscriptions
- Develop a storefront for an XaaS marketplace to increase customer service and loyalty
MSPs
- Capture higher margins on software and services versus hardware
- Selling solutions opens up new market opportunities and requires less headcount, enhancing scalability
- Stronger customer loyalty with less churn
IT DISTRIBUTORS
- Expand market share as an XaaS retailer while avoiding costly acquisitions if desired
- Use a hybrid delivery model of traditional and digital to increase revenue (9% growth on average)
- Increase customer loyalty and a more profitable return on capital employed (ROCE) with more offerings and operationally efficient digital distribution
ISVs
- Increase sales through the channel by following a subscription model
- Improve efficiency by standardizing integrations with partners using a management subscription platform
- Merge direct and indirect systems to streamline operations
TECH VENDORS
- Increase adoption of solutions and revenue through third-party bundles
- Connect with different players across the supply chain
- Increase differentiation in the market for your solutions